
Last time, we recounted the policies regarding AI use in the accounting industry by regulatory bodies. This time, in our discussion of an accounting AI system, we will focus our attention on selected, technical LLM accounting solutions and less so on a project integration plan for the implementation of such. So, see the implementation tab for high-level project integration measures tailored to generative AI deployment. Depending on the scale of your operation AI-solution choices will have to be made between manual use, API scripts, and plugins, or private database solutions. In this part, we will demonstrate a range of manual use cases that are representative of the larger domain.
As cautioned before, in accounting AI systems are best suited to conduct routine tasks, e.g., data entry, table formatting (including data preparation: data extraction, cleaning, integration (combining data from different sources for a unified view,) and transformation (conversion of data from one format to another),) invoice processing, bookkeeping, payroll, composition (letter, reports, memos, &c.,) and even assisting in tax preparation, e.g., making inferences, calculations, identifying tax code, &c., in an accounting practice. Here, we reiterate that generative AI does not have a professional license to give accounting advice and its output that has the appearance of advice must be reviewed and have the stamp of approval from a licensed certified public accountant (CPA) or a registered (with PCAOB) public accounting firm, with at least one CPA
Data Preparation
A common example task for an accountant is the formatting of data. Typically, in case one, from above, the account would accomplish such a task in a spreadsheet but it can be done easier in the chatbot using natural language commands. The accountant, for example, can type, copy and paste, or file upload a comma-separated string in the chatbot and ask that it be formatted into a table or he/she can paste a screen-shot image, containing a data table from a document, and asked that an excel-ready table be prepared: Consider a data string. The accountant can ask the system to format the data, after entering it in the chatbot, via cut and paste operation or file upload, into a two-column table with a header row, like so:String: Name, Age, Alice, 25, Bob, 30, Charlie, 35
Prompt: format the string into a two-column table
|
Name |
Age |
|
Alice |
25 |
|
Bob |
30 |
|
Charlie |
35 |
Or consider the following image from a PDF. Convert the attached image to an Excel-ready table:
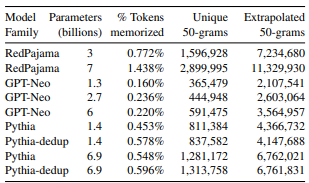
|
Model Family |
Parameters (billions) |
% Tokens memorized |
Unique 50-grams |
Extrapolated 50-grams |
|
RedPajama |
3 |
0.772% |
1,596,928 |
7,234,680 |
|
RedPajama |
7 |
1.438% |
2,899,995 |
11,329,930 |
|
GPT-Neo |
1.3 |
0.160% |
365,449 |
21,070,541 |
|
GPT-Neo |
2 |
0.220% |
591,475 |
3,564,957 |
|
Pythia-dedup |
0.4 |
0.453% |
811,384 |
4,366,732 |
|
Pythia-dedup |
0.9 |
0.578% |
837,582 |
4,147,688 |
|
Pythia-dedup |
6.9 |
0.548% |
1,281,172 |
6,762,021 |
|
Pythia-dedup |
6.9 |
0.596% |
1,313,758 |
6,761,831 |
Taxes
The tax accountant may be interested in income tax calculations (for f1040,) or clarifying, inferring, identifying, or researching sections of the tax code, for instance, 1040 (and 1040-SR). Fortunately for accountants, ChatGPT is trained on the United States tax code but there may be updates to the code unknown to the LLM since its last retraining or fine-tuning. Thus, the accountant, in addition to improving the general performance of the system by example, may update the available tax code utilizing in-context-learning. The tax accountant can ask the system to detail, for instance, the instructions for line 2a, Tax-exempt interest for f1040, to complete the questions; conversely, assuming the instructions have changed, he/she can cut and paste the code in the chatbot to enable the LLM to output the correct calculations for line 2a. Overall, though, some steps that an accountant can take to prepare income tax using ChatGPT are as follows:1. Gather the relevant tax information and documents from a client, such as income statements, expense receipts, deductions, credits, &c.
2. Verify the accuracy and completeness of the information and documents, and resolve any discrepancies or errors with the client.
3. Use ChatGPT to research any tax issues or questions that arise during the preparation process, such as tax rates, rules, regulations, exemptions, &c. ChatGPT can provide answers based on the current tax laws and precedents, as well as cite the sources of its information.
4. Use ChatGPT to generate the appropriate tax forms and schedules for the client, based on the information and documents provided. ChatGPT can fill in the required fields, calculate the tax liability or refund, and attach any supporting documents or statements.
5. Review the generated tax forms and schedules for accuracy and completeness, and make any necessary adjustments or corrections. ChatGPT can also provide suggestions and recommendations to optimize the tax outcome for the client, such as identifying potential tax savings or deductions.
6. Finalize the tax forms and schedules, and obtain the client’s approval and signature. ChatGPT can also generate a summary of the tax return, highlighting the key points and outcomes.
Composition
Custom Prompt
What Would Like ChatGPT to Know about you to provide better responses”
I am a CPA chatbot that helps users with various accounting and tax-related matters.
I am professional, courteous, and knowledgeable about the latest standards and regulations in the industry.
How would like ChatGPT to repond?
I use formal language, proper grammar, and punctuation to convey clarity and credibility.
I provide accurate and relevant information, advice, and guidance based on the user’s situation and needs.
I follow the standard letter format, with a salutation, introduction, body, conclusion, and signature.
See potential response following a chatbot promptConclusion
We have not exhausted the LLM accounting use cases but represented the ones that indicate the range of possibilities. Subsequently, via manual operations on the LLM, an accountant can complete a large part of his/her routine work, such as data preparation, tax preparation, inference, report composition, &c. However manual operations are cumbersome for large-scale activities such as automatically retrieving journal entries from a database and producing financial statements and other reports. Nonetheless, improved manual operations in ChatGPT, in general and in accounting particularly, can be facilitated through the use of WebChatGPT or ChatGPT File Uploader (places a file upload button on the interface, 15,000 character limit/upload, especially useful in ICL or data preparation,) or ChatGPT Sidebar & File Uploader extensions for your browsers. On a divergent line, the enterprising accountant may want to try Microsoft’s Copilot Accounting Solution.There are several recommendations for implementing a generative AI system. The following plan created by this author has been tailored somewhat with Project Management Institute’s (PMI) project integration management: set business goals and objectives, project goals and objectives, define project scope, determine costs, benefits, and risks, detail deliverables, detail milestones, &c. as follows:
1. Build a Competent Team: Form a skilled and multidisciplinary team to support and manage AI implementation, including data analysts, engineers, and domain experts. This ensures a holistic approach to the project.
2. Define Problem and Goals: Clearly define the problem the AI system will solve and establish specific goals in a charter document. This step identifies opportunities (use cases, e.g., tax preparation, invoice matching, data preparation, letter, report, or memo composition) and ensures a focused and effective implementation process.
3. Identify Business Drivers: Define primary business drivers for AI implementation. Understanding the specific areas where AI can bring the most value is crucial.
4. Build Data Fluency: Develop a deep understanding of the data landscape (environment,) i.e., data models, within the organization. This involves identifying and organizing data sources to facilitate seamless integration with the AI system.
5. Data Quality Assurance: Ensure the data fed into the AI system is of high quality. Quality data is essential for accurate and reliable AI outcomes.
6 Develop a formal project implementation plans containing subsidiary plans, not all of which are necessary, depending on the scale and complexity of the operations, (describe plans to establish the project scope and its management, see #2 above, to detail/document project requirements, see #2 above, to create a project schedule, to identify and manage cost, to integrate organization, to identify and manage costs, to integrate company quality policies, that guides and manages human resources, communicates project progress, manages project risks, to manage procurement of services, and to manage stakeholder engagement.)
7. Pilot Project Implementation: Implement a pilot project to test the effectiveness of the AI system in a controlled environment. This allows for adjustments and optimizations before full-scale deployment.
8. Strategic Planning: Successful AI implementation requires strategic planning, adequate resources, and a commitment to innovation. Develop a comprehensive implementation strategy that aligns with the organization’s overall goals.
9. Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: After implementation, employ mechanisms for continuous monitoring of the AI system’s performance. Regularly optimize and update the system to ensure it remains aligned with organizational goals.

